Describe the Location and Function of the Visual Association Area
Straight from Cogs 107A lecture know this Location. Primary Visual Cortex Note the crossing of optic nerves at optic chiasm and continuation as optic tracts.

Occipital Lobe Definition Functions And Location Simply Psychology
It is in the occipital lobe of the primary cerebral cortex which is in the most posterior region of the brain.

. Somesthetic association area function integrate and analyzes different somatic sensory inputs into comprehensive evaluation of what is being felt visual association area location. Receives tactile information from the body. They result from an inability to perceive objects despite normally functioning sensory systems.
Association areas interpret sensory experiences and remember visual scenes music and other complex sensory patternsOccipital lobes - sensory areas are. Therefore these areas are called somatosensory association areas. In the temporal lobes association areas function primarily in memory processes such as helping to process procedural and episodic memories.
Translates plans from M1 into specific instructions timing helps control saccades compares current motor plan to new plans sent from other brain areas. This associationarea lies in the large parietal and occipital cortical space bounded by the somatosensory cortex anteri-orly the visual cortex posteriorly and the auditory cortex laterally. They are represented by light blue in diagrams.
Stores visual memories Location of auditory association area. A small segment is. Initiation of voluntary movement.
Hubel. Coordination of complex movement. Association areas within the parietal lobe are involved in spatial skills such as spatial awareness and reasoning as well as being responsible for paying attention to visual stimuli in the environment.
Association areas integrate incoming sensory information and also form connections between sensory and motor areas. Brodmanns areas 5 and 7 of the cerebral cortex located in the parietal cortex behind somatosensory area I see Figure 475 play important roles in deci-phering deeper meanings of the sensory information in the somatosensory areas. Other articles where association area is discussed.
Detection of simple visual stimuli. It is thought that these areas integrate sensory and motor information and that this integration allows objects to be recognized and located in space. Describe white matterwhat it is and what its function isand give an example.
It receives strong feedforward connections from V1 direct and via the pulvinar and sends strong connections to. Processing of multisensory information. Striate cortex part of the occipital lobe that receives the fibers of the optic radiation and serves as the primary receiving area for vision.
Parts of the cerebral cortex that receive inputs from multiple areas. Each primary sensory area has an association area that it projects to. Function of visual association area 2 Allows for identificationunderstanding of objects through sight.
These include simple complex and higher lower order hypercomplex cells which. Kaas. Located just above the brainstem beneath the occipital lobes at the base of the skull.
Because they are involved in organizing information that comes from various other areas of the brain association areas are often linked to complex functions. The visual cortex is made up of a variety of cell types each of which is concerned with the analysis of different visual features Ferster et al 1996. Interprets information from the primary auditory cortex as pitch loudness and location.
The visual cortex is the primary cortical region of the brain that receives integrates and processes visual information relayed from the retinas. Visual area V2 or secondary visual cortex also called prestriate cortex is the second major area in the visual cortex and the first region within the visual association area. The striate cortex is also called the first visual area and the adjacent second and third visual areas serve as its association areas.
Visual image processing begins in the primary visual cortex V1 which is primarily located along the superior and inferior sides of the calcarine fissure on the medial side of the occipital lobe Broadmann area 17. Uses past visual experiences to interpret visual stimuli received by the primary visual cortex. General organization of perceptionof the cortex traditionally called association areas.
The prefrontal cortex somatosensory area the RAS Wernickes area the basal nuclei and the visual association area. Functional Neuroanatomy Of The Visual Association Areas 18 And 19. As would be expected it provides a high level of interpretative meaning for signals from all the surrounding sensory areas.
Parietal Association Cortex Mediates Spatial Orientation. Association areas give meaning to sensations. Some of these are unimodal grading into the visual association areas of the occipital and temporal lobes the auditory association areas of the temporal lobe and somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus.
The posterior parietal cortex the part of the parietal lobe posterior to S1 is filled with association areas. Called also first visual area. Visual cortex the area of the occipital lobe of the cerebral cortex concerned with vision.
Complex processing of visual information. Association areas - definition. The multimodal posterior association area receives inputs from the visual and auditory systems and from the hippocampus.
Hearing The primary auditory cortex is located on the transverse gyri that lie on the back of the superior temporal convolution of the temporal lobes. The visual area is located on the calcarine sulcus deep within the inside folds of the occipital lobe. With these regions acting upon all their inputs the brain is carrying out.
Describe the specific location and function of each of the following.

Frontal Lobe Function Google Search Frontal Lobe Function Brain Anatomy Brain Lobes

Functional Areas Diagram I Motor Areas Posterior Part Of The Frontal Lobes Primary Motor Cortex Precentral Gyru Motor Cortex Cerebral Cortex Brain Diagram

Pin By Romee Bras On School Studying Brain Anatomy Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Science

Visual Processing Pics Visual Processing Brain Williams Syndrome Visual Cortex Teaching Math

Functional Areas Of The Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex Function Basic Anatomy And Physiology

Cerebral Cortex Location Functions Simply Psychology

Functional Systems Of The Cerebral Cortex Boundless Anatomy And Physiology

Location And Function Of The Parts Of The Cerebrum Google Search Brain Structure Brain Parts And Functions Central Nervous System

Your Brain Structure What Is The Brain Made Of Brain Structure Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Health Nutrition

Macho Switch In The Brain That Makes Men Aggressive Is Pinpointed Primary Motor Cortex Motor Cortex Motor Cortex Function

Cerebral Cortex Location Functions Simply Psychology

Difference Between Broca S Area And Wernicke S Area In The Brain Wernicke S Area Broca S Area Brain Anatomy And Function

Log On To Constellation Anatomy And Physiology Brain Anatomy Brain Diagram
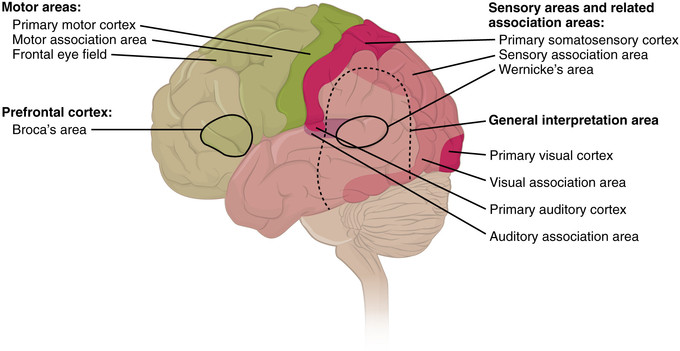
Functional Systems Of The Cerebral Cortex Boundless Anatomy And Physiology

Anatomy And Functional Areas Of The Brain Doctor Stock Human Brain Anatomy Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Anatomy

Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex Function Brain Cortex

Interesting Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Anatomy Brain Structure


Comments
Post a Comment